Embark on a culinary adventure with our comprehensive vegetarian nutrition plan, meticulously crafted to empower you with the knowledge and tools to thrive on a plant-based diet. Discover the secrets to meeting your unique nutritional needs, exploring a world of vibrant flavors and wholesome ingredients.
Delve into the intricacies of vegetarian nutrition, unraveling the mysteries of protein, iron, calcium, and vitamin B12. We’ll guide you through the principles of creating a balanced meal plan, ensuring you savor every bite while nourishing your body from within.
Nutritional Needs of Vegetarians
Vegetarian diets offer numerous health benefits, but meeting nutritional requirements is crucial. Vegetarians have unique needs for specific nutrients, including protein, iron, calcium, and vitamin B12.
Adopting a vegetarian diet can bring numerous health benefits, and finding delicious and nutritious meal options is key. Explore vegetarian diet ideas that cater to your taste buds while providing essential nutrients.
Protein
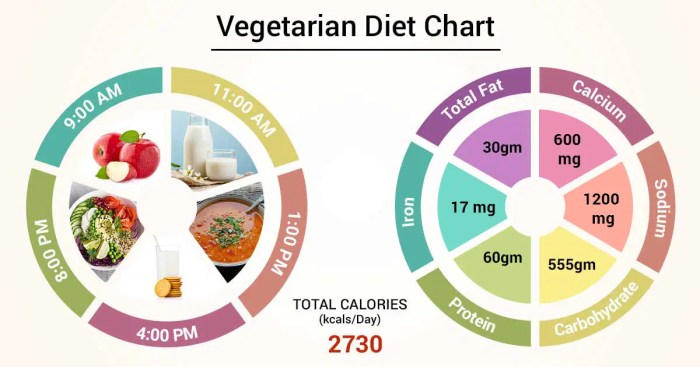
Protein is essential for building and repairing tissues. Vegetarians can obtain protein from plant-based sources such as legumes, beans, lentils, tofu, tempeh, nuts, and seeds. Aim for a daily intake of 0.8-1 gram of protein per kilogram of body weight.
Iron
Iron is necessary for red blood cell production. Vegetarians may have lower iron absorption than meat-eaters. Good sources of iron include fortified cereals, leafy green vegetables, beans, and lentils. Aim for a daily intake of 18 mg for women and 8 mg for men.
Calcium
Calcium is crucial for bone health. Vegetarians can get calcium from dairy alternatives such as fortified plant-based milk, yogurt, and cheese, as well as leafy green vegetables, tofu, and fortified cereals. Aim for a daily intake of 1,000-1,200 mg.
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is essential for nerve function and red blood cell production. Vegetarians cannot obtain B12 from plant sources, so it’s crucial to consume fortified foods or supplements. Aim for a daily intake of 2.4 mcg.
Other essential nutrients for vegetarians include:
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Found in flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts
- Zinc: Found in beans, nuts, and fortified cereals
- Iodine: Found in iodized salt and seafood
- Vitamin D: Found in fortified plant-based milk and fatty fish
Protein Sources for Vegetarians

Plant-based proteins are essential for vegetarians as they provide the body with the amino acids it needs to function properly. There are many different plant-based sources of protein available, each with its own unique nutritional profile.
Embark on a culinary journey with vegetarian diet ideas that tantalize your taste buds. From hearty tofu stir-fries to savory lentil soups, the possibilities are endless. Whether you’re a seasoned veggie lover or just starting to explore the world of plant-based eating, these recipes will inspire you to create delicious and nutritious meals that nourish your body and satisfy your cravings.
Some of the best plant-based sources of protein include:
- Beans: Beans are a good source of protein, fiber, and iron. They are also low in fat and calories.
- Lentils: Lentils are another good source of protein, fiber, and iron. They are also a good source of folate and potassium.
- Tofu: Tofu is a versatile plant-based protein source that can be used in a variety of dishes. It is a good source of protein, iron, and calcium.
- Tempeh: Tempeh is a fermented soybean product that is a good source of protein, fiber, and iron. It is also a good source of probiotics.
- Nuts: Nuts are a good source of protein, fiber, and healthy fats. They are also a good source of vitamins and minerals.
Table of Protein Content and Nutritional Value of Plant-Based Protein Sources
The following table compares the protein content and nutritional value of various plant-based protein sources:
| Protein Source | Protein (g/100g) | Calories (kcal/100g) | Fat (g/100g) | Carbohydrates (g/100g) | Fiber (g/100g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beans | 21 | 330 | 1.5 | 60 | 15 |
| Lentils | 26 | 350 | 1.5 | 60 | 18 |
| Tofu | 8 | 70 | 4 | 1 | 1 |
| Tempeh | 19 | 190 | 10 | 9 | 5 |
| Nuts | 15-20 | 550-650 | 45-60 | 15-20 | 5-10 |
Iron Absorption in Vegetarian Diets
Iron is an essential mineral that plays a crucial role in oxygen transport, energy production, and immune function. However, vegetarians may face challenges in meeting their iron needs due to the lower bioavailability of iron from plant sources compared to animal sources.
The absorption of iron from plant foods is influenced by several factors, including the type of iron present, the presence of enhancers and inhibitors, and the overall composition of the diet. Heme iron, found in animal products, is more readily absorbed than non-heme iron, which is found in plant foods.
Enhancing Iron Absorption
To enhance iron absorption from vegetarian diets, it is important to consume a variety of iron-rich plant foods and combine them with sources of vitamin C. Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, helps convert non-heme iron into a more absorbable form.
- Iron-rich plant foods:Legumes (beans, lentils, peas), leafy green vegetables (spinach, kale), fortified cereals, and tofu are excellent sources of non-heme iron.
- Vitamin C sources:Citrus fruits (oranges, grapefruits), berries (strawberries, blueberries), bell peppers, and tomatoes are rich in vitamin C.
Combining iron-rich foods with vitamin C sources in the same meal can significantly improve iron absorption. For example, adding lemon juice to a lentil soup or having a glass of orange juice with a spinach salad can enhance the absorption of iron from these plant-based sources.
Calcium and Vitamin B12 Considerations: Vegetarian Nutrition Plan

Calcium is crucial for strong bones, teeth, and nerve function. Vitamin B12 supports the nervous system and red blood cell production. Vegetarians may need to pay special attention to their intake of these nutrients.
Calcium Sources, Vegetarian nutrition plan
Dairy products are excellent sources of calcium. Fortified plant-based milks, juices, and cereals also provide significant amounts. Leafy green vegetables like kale and spinach contain calcium, but their absorption is lower due to the presence of oxalates.
Vitamin B12 Sources
Vitamin B12 is primarily found in animal products. Vegetarians can obtain it from fortified foods such as plant-based milks, cereals, and nutritional yeast. Supplementation may also be necessary to ensure adequate intake.
Meal Planning and Recipe Ideas
Planning and preparing vegetarian meals can be enjoyable and rewarding. Here are some tips to help you get started:
To ensure a balanced intake of nutrients, plan meals that include a variety of foods from all food groups. This includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. Consider incorporating a variety of colors and textures into your meals to enhance both visual appeal and nutrient diversity.
Meal Prepping and Cooking Techniques
- Meal prepping can save time and effort throughout the week. Dedicate a specific time each week to plan your meals, prepare ingredients, and cook in bulk. This will make it easier to assemble meals throughout the week.
- Use a variety of cooking techniques to keep meals interesting. Consider grilling, roasting, steaming, stir-frying, and baking. Experiment with different flavors and spices to create flavorful and satisfying dishes.
Vegetarian Recipe Collection
Here are some healthy and flavorful vegetarian recipes to inspire your meal planning:
- Breakfast:Oatmeal with berries and nuts, tofu scramble with vegetables, whole-wheat toast with avocado and hummus
- Lunch:Lentil soup with whole-wheat bread, grilled veggie sandwich on whole-wheat bread, salad with quinoa, chickpeas, and vegetables
- Dinner:Vegetarian chili with cornbread, lentil shepherd’s pie, stir-fried vegetables with brown rice
- Snacks:Apple slices with peanut butter, trail mix, yogurt with berries
Last Recap
As you embrace this vegetarian odyssey, remember that knowledge is your compass. With careful planning and a touch of culinary creativity, you’ll unlock a symphony of flavors and textures that will redefine your perception of plant-based cuisine. Let this guide be your beacon, illuminating the path to a vibrant and fulfilling vegetarian lifestyle.
User Queries
Can vegetarians get enough protein?
Absolutely! Plant-based sources like beans, lentils, tofu, tempeh, and nuts provide ample protein. Combining different sources throughout the day ensures you meet your daily protein needs.
How can vegetarians improve iron absorption?
Pair iron-rich plant foods like spinach, lentils, and fortified cereals with vitamin C sources like citrus fruits, bell peppers, and tomatoes. This enhances iron absorption and optimizes your body’s utilization of this essential mineral.
What are good sources of calcium for vegetarians?
Leafy green vegetables like kale, collard greens, and bok choy are excellent sources of calcium. Fortified plant-based milk, yogurt, and tofu also contribute to your daily calcium intake.